PlantSimEngine.jl
Purpose
PlantSimEngine is a package for the simulation and modelling of plants, soil and atmosphere. It is designed to help researchers and practitioners prototype, implement, test plant/crop models at any scale, without the hassle of computer science technicality behind model coupling, running on several time-steps or objects.
The package defines a framework for declaring processes and implementing associated models for their simulation.
It focuses on key aspects of simulation and modeling such as:
- Easy definition of new processes, such as light interception, photosynthesis, growth, soil water transfer…
- Fast, interactive prototyping of models, with constraints to help users avoid errors, but sensible defaults to avoid over-complicating the model writing process
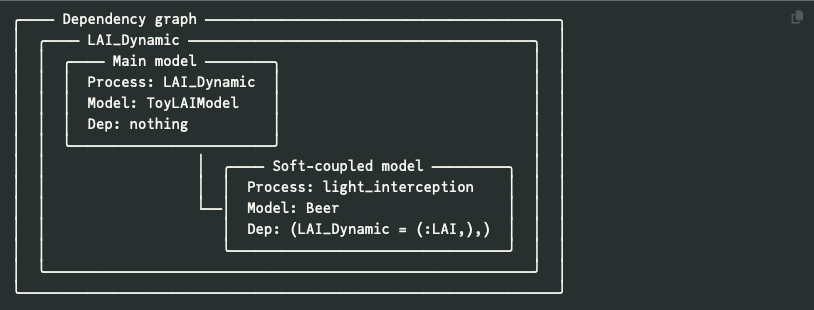
- No hassle, the package manages automatically input and output variables, time-steps, objects, soft and hard coupling of models with a dependency graph
- Switch between models without changing any code, with a simple syntax to define the model to use for a given process
- Reduce the degrees of freedom by fixing variables, passing measurements, or using a simpler model for a given process
- 🚀(very) fast computation 🚀, think of 100th of nanoseconds for one model, two coupled models (see this benchmark script ), or the full energy balance of a leaf using PlantBiophysics.jl that uses PlantSimEngine
- Out of the box Sequential, Parallel (Multi-threaded) or Distributed (Multi-Process) computations over objects, time-steps and independent processes (thanks to Floops.jl )
- Easily scalable, with methods for computing over objects, time-steps and even Multi-Scale Tree Graphs
- Composable, allowing the use of any types as inputs such as Unitful to propagate units, or MonteCarloMeasurements.jl to propagate measurement error
Try it !
Start by creating a new environment for your project using the pkg manager. To enter the package manager, just press ] in the REPL, and it will become blue (press backspace to return to the Julia REPL). Then create the environment using this command:
activate .
Don’t forget the “.”! It is used to tell the pkg manager that you activate the project were you currently are.
You can then install PlantGeom using this command (still from the pkg manager):
add PlantSimEngine
Example
Here’s a simple example of a model that simulates the growth of a plant, using a simple exponential growth model:
# ] add PlantSimEngine
using PlantSimEngine
# Import the examples defined in the `Examples` sub-module
using PlantSimEngine.Examples
# Define the model:
model = ModelList(
ToyLAIModel(),
status=(TT_cu=1.0:2000.0,), # Pass the cumulated degree-days as input to the model
)
run!(model) # run the model
status(model) # extract the status, i.e. the output of the model
LICENSE
This package is distributed under the MIT license. A full description of the license can be found here .
Links
- Link to github
- Link to the official documentation
Reference
Vezy, R., (2023). PlantSimEngine: A Simulation Engine For The Soil-Plant-Atmosphere System. Journal of Open Source Software, 8(86), 5371, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.05371